Unlocking the Power of Hot Chamber Die Casting: The Ultimate Guide
Imagine manufacturing thousands of precision metal parts with minimal waste and maximum efficiency. Hot chamber die casting is the key process behind high-quality, complex metal components that are integral to industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. By utilizing advanced technology and low-melting point alloys, hot chamber die casting delivers rapid, high-volume production with remarkable precision.
Let’s dive into how this process works, its applications, and the distinct advantages that make it a go-to method for metal casting.
What is Hot Die Casting?
Hot die casting is a specialized method for creating parts by injecting molten metal into a mold under high pressure. Unlike cold chamber die casting, where molten metal is transferred from an external furnace, hot chamber die casting involves a furnace integrated within the machine, where metal is melted and injected directly into the mold.
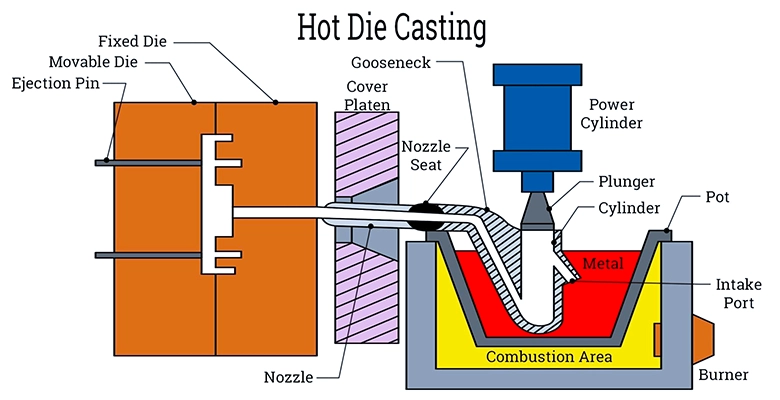
How it works:
hot chamber die casting process
Molten Metal: The process begins with the metal being melted inside a furnace integrated into the die casting machine. The furnace is equipped with a ladle or gooseneck system that ensures molten metal is always available for injection.
Injection: Once the metal is molten, a gooseneck or plunger mechanism moves the metal into the mold cavity. The pressure applied typically ranges from 1,500 to 25,000 psi, ensuring that the molten metal fills every crevice of the mold with precision.
Cooling and Ejection: After injection, the molten metal cools and solidifies, taking on the shape of the mold. The mold is then opened, and the solidified part is ejected.
The hot chamber die casting process is ideal for metals with lower melting points, such as zinc, magnesium, lead, and tin alloys. These metals are often chosen because they flow easily when molten, allowing for faster cycle times and more intricate part designs.
Why Choose Hot Chamber Die Casting?
Hot chamber die casting provides numerous advantages that make it perfect for high-volume production. Whether manufacturing intricate automotive parts, tiny electronic components, or household items, this method ensures consistently high-quality results.
Key Benefits of Hot Chamber Die Casting: Faster Cycle Times: Integrating the furnace with the die-casting machine allows for quicker metal melting and continuous operation. This efficiency makes hot chamber die casting an optimal choice for rapidly producing components.
Precision and Detail: It achieves remarkable precision and is ideal for applications demanding tight tolerances and detailed intricacies. The high pressure during injection guarantees that even the tiniest features are accurately replicated in the finished product.
High-Quality Surface Finishes: The process yields smooth, polished surfaces that generally need little to no additional finishing. Thus, it is particularly suitable for parts designed for visible or high-performance purposes.
Durability and Strength: Hot chamber die casting components are known for their strength and sturdiness. The technique employs high-pressure injection to create solid, dense parts that can withstand wear and stress.
Cost-Effective for High Volumes: This process is exceptionally efficient for large production runs, as tooling costs can be spread over many parts, reducing the cost per unit. Its speed and short cycle times further enhance cost savings, making it an exceptional choice for high-volume manufacturing.
Material Flexibility: Hot chamber die casting accommodates metals with low melting points like zinc, magnesium, and lead alloys, which are perfect for producing parts that are strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant.
Minimal Waste: The method generates minimal waste since the metal is injected directly into the mold with minimal excess, contributing to the process’s overall sustainability.
Limitation
Limitations of Hot Chamber Die Casting
• Limited to Low-Melting Alloys: The process can only be used for metals like zinc and tin. Alloys with higher melting points, such as aluminium, would damage the equipment.
• Limited Part Size: Hot chamber die casting is suitable for small to medium-sized parts but not for larger or heavier components.
• Corrosive Wear on Equipment: Low-melting alloys, particularly zinc-aluminium, can cause corrosion over time, leading to increased maintenance costs.
Applications of Hot Chamber Casting
Hot chamber casting is used in various industries due to its precision and efficiency. Some of the most common applications include
Automotive Industry
Zinc die castings are used in various automotive parts, such as powertrain components, door locks, and interior trim.
Magnesium alloys are also used for lightweight automotive components, reducing the overall weight of vehicles while maintaining strength.
Electronics Industry
Hot chamber die casting is ideal for producing electronics enclosures, connectors, and housings. The process allows for detailed, high-precision components that protect sensitive equipment.
Consumer Goods
Household items such as faucets, lock bodies, and decorative components benefit from the smooth surfaces and intricate shapes achievable through hot chamber die casting.
Industrial Equipment
Because of the strength and durability of the material, hot chamber casting frequently produces parts like electrical connectors, valves, and hardware.
Ready to discuss your project?
Request a quote online and let’s bring your ideas to zinc castings.
Hot Chamber vs. Cold Chamber Die Casting: Key Differences
While both hot chamber and cold chamber die casting involve the injection of molten metal into molds, there are significant differences between the two processes.
| Feature | Hot Chamber Die Casting | Cold Chamber Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Type | Ideal for low melting point metals (zinc, magnesium, lead) | Ideal for high melting point metals (aluminum, brass, copper) |
| Furnace | Furnace is integrated into the machine | Furnace is separate from the machine |
| Injection Process | Continuous injection of molten metal from the furnace | Molten metal is ladled into the machine |
| Cycle Time | Faster cycle times | Slower cycle times |
| Tooling Costs | Generally lower tooling costs | Higher tooling costs |
| Maintenance | More frequent maintenance due to exposure to molten metal | Less frequent maintenance |
Solution for Precision Manufacturing
Hot chamber die casting is the go-to method for manufacturing high-precision, high-quality metal parts at scale. Whether you’re in the automotive, electronics, or consumer goods industry, this process ensures your parts are produced with speed, durability, and minimal waste.


















No comment