Die-Cast Aluminum vs. Cast Aluminum: A Comprehensive Guide
Aluminum is one of the most versatile and widely used materials in modern manufacturing. From the automotive and aerospace industries to consumer electronics and home appliances, aluminum’s lightweight and durable properties make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. However, understanding the manufacturing processes behind aluminum products is essential for selecting the right method for your project. In this guide, we’ll explore the differences between die-cast aluminum and cast aluminum, highlighting their advantages, limitations, and ideal applications.
What is Cast Aluminum?
Cast aluminum refers to aluminum products that are manufactured using various casting techniques. These processes involve pouring molten aluminum into a mold, which cools and solidifies into the desired shape. The most common casting methods include:
Sand Casting: Involves pouring molten aluminum into a sand mold, making it ideal for large, simple parts.
Gravity Casting: Relies on gravity to fill the mold with molten aluminum, commonly used for parts with moderate complexity.
Permanent Mold Casting: Uses a reusable metal mold and is typically suited for higher-volume production of medium-sized parts.
Ceramic Mold Casting: Also known as investment casting, this method is ideal for highly detailed, precision parts.
Each casting process has its own advantages. Sand casting and gravity casting are more cost-effective for low-to-medium volume production, while permanent mold casting and ceramic mold casting are better suited for high-precision parts.
What is Die-Cast Aluminum?
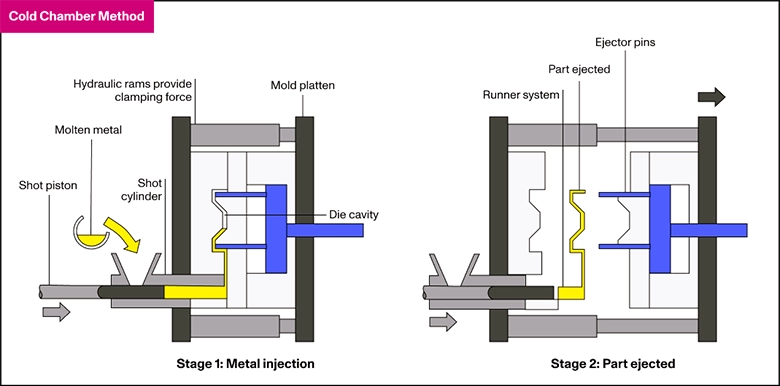
Die-cast aluminum is a high-pressure casting process where molten aluminum is injected into a steel mold (die) at extremely high pressures. The die quickly solidifies the aluminum, producing a precise, high-quality part. This process is commonly used for manufacturing components with complex geometries and is highly favored in industries that require large-volume production.
Key Advantages of Cast Aluminum
Cast aluminum products offer several benefits, including:
Strength and Durability: Cast aluminum parts are strong and can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for a wide variety of applications.
Lightweight: Aluminum’s low density ensures that cast parts remain lightweight, making them ideal for industries like automotive and aerospace, where weight is a crucial factor.
Cost-Effectiveness: The casting process is relatively low-cost, especially for low-to-medium volume production, making it an ideal choice for budget-conscious projects.
Heat Resistance: Cast aluminum is highly resistant to heat, making it perfect for high-temperature applications such as home appliances and cooking ranges.
Key Advantages of Die-Cast Aluminum
Die-cast aluminum stands out due to its precision and suitability for high-volume production. Some of the primary benefits include:
Complex Geometries: Die-casting allows for the creation of highly detailed and intricate parts, which would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional casting methods.
Consistency and Accuracy: The high-pressure process ensures that parts are dimensionally accurate with tight tolerances, making them ideal for automotive electronics, consumer goods, and LED housings.
Thin Walls: Unlike other casting methods, die casting can produce components with very thin walls, which is especially beneficial for lightweight designs.
High Volume: Due to its efficiency, die-casting is ideal for large-volume production, making it the preferred method for industries that require hundreds or thousands of parts.
Factors Affecting the Choice Between Die-Cast and Cast Aluminum
When deciding between die-cast aluminum and cast aluminum, several factors must be considered:
Material Selection: The aluminum alloy chosen plays a significant role in determining the strength, corrosion resistance, and surface finish of the final product. For both methods, it is crucial to choose the appropriate alloy to meet the required performance standards.
Production Scale: Die-cast aluminum is most cost-effective for large-scale production runs, while cast aluminum is better for smaller runs due to its lower mold costs.
Mold Costs: The cost of molds is higher for die casting due to the use of durable steel molds, which are expensive to produce. However, this investment pays off in large-volume production.
Post-Casting Finishing: Both processes may require additional finishing steps such as machining, polishing, or coating to improve the surface finish or meet functional requirements. Die-cast aluminum often requires additional trimming or edge finishing due to the precision of the mold.
Discussing your project needs?
If you’re looking to produce high-quality aluminum components, BluNet offers expert manufacturing solutions in both die-cast and cast aluminum.
Which Process Should You Choose?
The decision between die-cast aluminum and cast aluminum depends on several factors, including production volume, complexity, and cost considerations:
Die-Cast Aluminum: Best suited for high-volume production of parts with complex geometries, tight tolerances, and thin walls. It’s ideal for automotive components, consumer electronics, and high-precision parts.
Cast Aluminum: Ideal for small to medium-volume production of simpler parts where cost-efficiency is a primary concern. It is frequently used for home appliances, furniture, and heavy-duty industrial components.
Both processes offer unique benefits, and choosing the right one for your project depends on the specific needs of your application. If you require high-precision and complex parts, die-cast aluminum is the way to go. However, if you are working with larger, less intricate components and need cost-effective production, cast aluminum may be more appropriate.
Conclusion
Both die-cast aluminum and cast aluminum play critical roles in the manufacturing of aluminum components across various industries. Understanding the key differences between the two methods will help you make the right choice for your production needs. Whether you need complex, high-volume parts or simpler, low-volume components, these casting methods provide versatile solutions for a wide range of applications.












No comment