Die Cast Aluminum Alloys – The Complete Guide
Die casting is a widely used manufacturing process for producing metal parts by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. Aluminum alloys are among the most popular materials for die casting due to their excellent properties, including high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ease of processing. Selecting the right aluminum alloy for die casting is crucial to ensure the final product meets the required specifications for strength, durability, and aesthetic appearance. This guide will explore the various aluminum alloys used in die casting, their benefits, limitations, common applications, and other important factors to consider when selecting the right alloy for your project.
Title Element
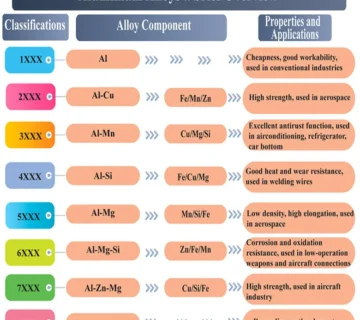
2. Which Grades of Aluminum Alloys Are Suitable for Die Casting?
There are several grades of aluminum alloys, each with distinct characteristics that make them suitable for specific die casting applications. The choice of alloy is based on factors such as the intended application, mechanical requirements, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Below is a closer look at some of the most commonly used aluminum alloys in die casting.
2.1 A380 Aluminum Alloy
Description and Benefits: A380 is a versatile aluminum alloy with excellent corrosion resistance, high operating temperatures, and good dimensional stability. It also offers strong thermal and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for parts exposed to elevated temperatures.
Applications: Commonly used for automotive parts like engine brackets, hand tools, electronic equipment, and other components that require high strength and wear resistance.
2.2 A383 Aluminum Alloy
Description and Benefits: A383 offers high corrosion resistance, good fluidity, and exceptional mechanical and thermal properties. It is widely used for casting intricate components and provides an excellent surface finish.
Applications: Typically used in the automotive and electronics industries for components such as motor vehicle parts, home appliances, and other precision-engineered components.
Limitations: It is less durable than A380, making it unsuitable for high-stress applications.
2.3 A360 Aluminum Alloy
Description and Benefits: A360 excels in corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments. It also offers superior strength at elevated temperatures and better ductility than some other alloys, making it an ideal choice for parts exposed to high thermal stresses.
Limitations: A360 can be difficult to cast due to its complex fluidity characteristics.
Applications: Used in automotive oil pans, 5G communication boxes, LED lamp housings, and other applications requiring high strength and durability.
2.4 B390 Aluminum Alloy
Description and Benefits: B390 is known for its high hardness and excellent wear resistance. It is commonly used in applications that require robust, high-performance materials.
Limitations: The alloy has lower density, and it is difficult to machine due to its hardness.
Applications: Used in engine pistons, compressors, and other heavy-duty applications requiring superior wear resistance.
2.5 A413 Aluminum Alloy
Description and Benefits: A413 is a high-performance alloy known for its excellent pressure tightness, corrosion resistance, and high specific strength. It provides exceptional castability, making it ideal for complex designs.
Limitations: The high cost and potential impurities can affect the alloy’s consistency.
Applications: Commonly used in aerospace, marine, automotive industries, and for gas and air cylinders.
2.6 A356 Aluminum Alloy
Description and Benefits: A356 offers excellent castability, good corrosion resistance, and excellent weldability. It is highly valued for producing complex, durable, and precision components.
Applications: Commonly used for truck chassis, pump bodies, and automotive transmission cases, among others.
2.7 A357 Aluminum Alloy
Description and Benefits: A357 is known for its high strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. It is used in applications requiring parts that need to perform under load and stress.
Applications: Often found in automotive frames and pump and valve components.
2.8 K Alloy / A304
Description and Benefits: K Alloy (or A304) offers excellent corrosion resistance without requiring additional surface finishing. It also provides superior flowability, which is important for die casting complex parts.
Applications: Commonly used for vehicle components, military equipment, and recreational vehicles.
Which Parts Can You Make From Die Cast Aluminum Alloys?
Die cast aluminum alloys are ideal for producing a wide range of parts, including those that require intricate designs and high mechanical properties. Common parts include:
- Engine Blocks: Essential for the automotive industry, providing strength and weight-saving benefits.
- Automotive Parts: Includes components like transmission cases, engine brackets, and intake manifolds.
- Firearms: High precision and durability for critical firearm components.
- Medical Equipment: Die castings are used in medical devices that require high-quality, corrosion-resistant materials.
- Lighting Enclosures: Aluminum alloys ensure long-lasting, robust housings for lighting fixtures.
- Industrial Equipment: Various complex components used in heavy machinery and industrial systems.
Die casting allows for the production of highly complex and precise parts, which is a significant advantage over other manufacturing processes.
Recommended Surface Finishes for Die Cast Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum die castings can undergo a variety of surface finishes to enhance their appearance, corrosion resistance, and functionality. Some of the most popular options include:
- Chrome Plating: Provides a high-quality, shiny finish suitable for automotive parts.
- Chromate: A cost-effective conversion coating available in various colors.
- Anodizing: Electrochemical process to enhance corrosion resistance and provide an aesthetic finish.
- Powder Coating: Durable, scratch-resistant coating ideal for industrial and decorative parts.
- E-coat: Offers corrosion resistance with an electrostatic painting method.
- Bright Nickel: Aesthetic finish for decorative items, though less durable.
- Polishing: Enhances reflectivity and reduces wear and corrosion.
- Painting: Customizable options for branding and design.
- Teflon Coating: Provides low friction and excellent corrosion resistance.
- Electroless Nickel Plating: Provides uniform coating without the need for a power supply.
- Chem Film: Conversion coating that improves corrosion resistance.
These finishes can help to improve the aesthetic and functional properties of die-cast aluminum alloys, ensuring the final product meets both design and performance requirements.
How to Choose a Mold for Die Casting Aluminum Alloy
Choosing the right mold for aluminum die casting is crucial for ensuring uniformity, high-quality output, and precision in the final product. Key factors to consider when selecting a mold include:
- Mold Material: Heat-resistant steel is commonly used for its durability under the high temperatures of the die casting process.
- Design Considerations: Ensure that the mold is designed for uniformity, repeatability, and accommodates the desired shape and configuration of the product.
- Precision: Molds should be carefully engineered to ensure consistent production quality across batches.
Improper mold specifications can lead to defects in the cast parts, resulting in costly rework and delays.
Do Die Cast Aluminum Alloys Require Heat Treatment?
Die casting can sometimes result in various defects, which can affect the quality and usability of the final product. Some common defects include:
- Internal Defects:
- Gas Porosity: Trapped gases create cavities in the alloy.
- Shrinkage Porosity: Caused by cooling and solidification, leading to voids in the cast.
- Inclusions: Non-metallic or intermetallic materials within the alloy, weakening the final product.
- Superficial Defects:
- Lakes: Aesthetic defects caused by uneven solidification.
- Cold Laps: Irregular flow leading to poor surface quality.
- Blisters: Air pockets trapped inside the mold, causing surface bubbles.
- Lamination: Overlapping layers within the cast, often difficult to detect.
- Cracks: Caused by residual stress or external forces during cooling.
These defects can significantly impact the strength and appearance of the parts, so attention must be given to process control and mold design.
7. Do Die Cast Aluminum Alloys Require Heat Treatment?
Heat treatment is often necessary for modifying the properties of die-cast aluminum alloys. The primary types of heat treatment include:
- Solution Annealing: Involves heating the alloy to a high temperature and then cooling it quickly to dissolve unwanted elements.
- Aging: A process that increases the strength of the alloy by allowing it to reach a higher hardness over time.
The choice to use heat treatment depends on factors like the intended purpose of the part, the manufacturing process, and the production environment. While heat treatment can improve properties such as strength and hardness, it can also increase production costs and turnaround time.
Selecting the right aluminum alloy for die casting is a crucial decision that affects the final product’s performance, appearance, and cost-efficiency. Understanding the properties, benefits, limitations, and applications of various alloys such as A380, A383, A360, and others will help ensure you choose the best material for your needs. Additionally, considering factors like mold selection, surface finishes, and common defects will improve the quality and durability of your die-cast parts. If you have any further questions or need expert advice on die casting, feel free to reach out for more information.














No comment