Zinc Die Casting
Precision, Economy,High‑Precision Parts at High Speed
Zinc die casting excels when your design requires tight tolerances, complex geometry, and attractive economics. Thanks to its low melting temperature, zinc allows for die tools that last up to ten times longer than those used for aluminium. It significantly reduces lifetime tooling costs while maintaining ±0.05 mm dimensional accuracy.
Since 2001, DSW Diecasting has produced precision zinc die-cast components for various sectors, including medical, electronics, automotive, microwave, and general hardware. Our decades of experience and technical expertise enable us to deliver complex, tight-tolerance parts promptly and cost-effectively.
Custom Zamak Parts
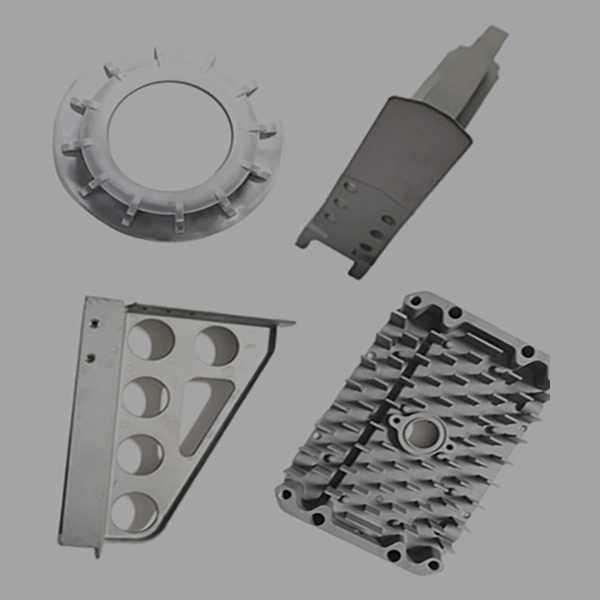

Advantages of Zinc Die Casting?
Sector Advantages Driving Adoption: The Go-To Solution for Precision Metal Parts
- Cost‑Effective Tooling —
Zinc’s low melting temperature lets a die last up to ten times longer than an aluminium one, slashing amortised tooling costs for mass production. - Design Freedom —
Cast ultra‑thin, intricate, near‑net shapes (often ≤ 0.5 mm walls) that would be impractical with aluminium or magnesium. - Mechanical Balance —
High yield strength, good elongation, and excellent vibration damping make zinc ideal for both structural and tactile components. - Finishing Versatility —
Takes plating, powder coating, e‑coating, PVD, and paint exceptionally well, delivering decorative appeal and robust corrosion resistance. - Fast Cycle Times —
Hot‑chamber presses inject, solidify, and eject within seconds, enabling high‑volume production with consistent quality.
Processing of Zamak Die Casting?
Provides hot chamber die casing for industries
Die casting is a precise manufacturing process that relies on different die types to produce high-quality parts.
Hot Chamber Dies
Used for metals with low melting points like zinc and magnesium, offering fast production.
Applications: Zinc die casting, small parts.
We employ both hot and cold chamber die casting techniques to meet diverse production requirements:
- Hot Chamber: Molten aluminum is injected into the hot chamber die through a gooseneck submerged in the molten metal, allowing for efficient production with high output rates.
Both methods ensure the production of high-quality parts with minimal cycle times.
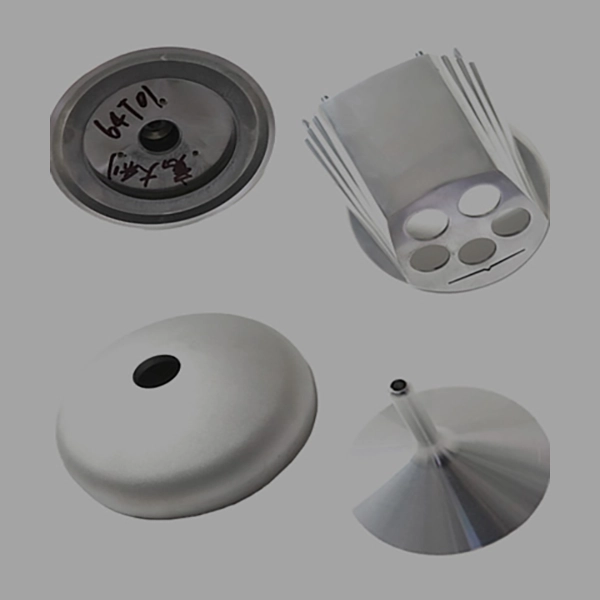
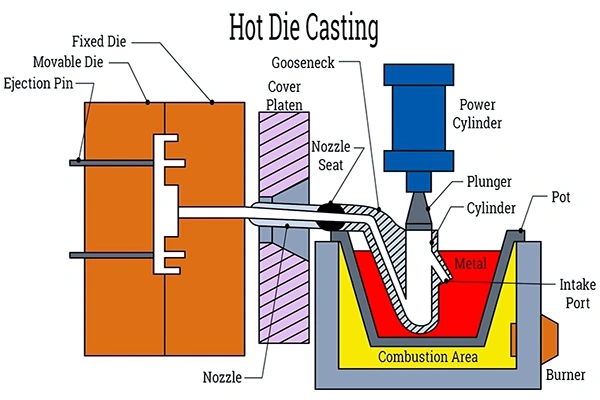

At DSW, we support you at every stage – from initial design and prototyping, through die manufacture and full‑scale casting, to post‑machining.
Working closely with you, we refine and optimise your design to ensure it is perfectly suited to zinc casting.
Zinc Alloys for Die Casting
unique blend of strength, detail, and cost‑effectiveness.
Zinc alloys combine exceptional mechanical strength with the ability to capture fine details—even at wall thicknesses under 0.5 mm. They offer superior impact resistance and dimensional stability, outperforming many aluminium and plastic parts in rigorous service conditions.
Principal Zinc Alloys Used in Pressure Die Casting
| Alloy (UK / ISO designation) | Nominal Composition (wt %) | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zamak 3 (ZL0400 / ZP3) | Zn, Al 4 %; trace Mg | Benchmark castability; plates exceptionally well; good ductility for crimping / swaging | Decorative fittings, consumer‑electronics frames, small automotive clips |
| Zamak 5 (ZL0410 / ZP5) | Zn, Al 4 %; Cu 1 %; trace Mg | c. 15 % higher tensile strength and improved hardness over Zamak 3; slightly reduced elongation | Door‑lock housings, lever handles, structural brackets |
| Zamak 7 (ZL0430 / ZP2) | Zn, Al 4 %; lower Mg than Zamak 3 | Highest fluidity within the Zamak range; excellent for thin‑wall, fine‑detail castings | Precision miniature components, tight‑tolerance electrical connectors |
| ZA 8 (ZL0810) | Zn, Al 8 %; Cu 1 % | Hot‑chamber compatible; superior strength‑to‑weight ratio and enhanced creep resistance | Automotive actuator gears, pneumatic valve bodies |
| ZA 12 (ZL1210) | Zn, Al 11 %; Cu 1 % | Suited to gravity or cold‑chamber casting; outstanding bearing characteristics | Heavy‑duty industrial housings, wear bushings |
Diverse applications
| Sector | Typical Components | Why Zinc Is Preferred |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive & Mobility | Door‑lock housings; window cranks; seat‑belt buckles; sensor brackets; EV charging‑port latches | Excellent strength‑to‑weight ratio; high dimensional accuracy for mating parts; inherent vibration damping; superior plating quality for visible interior pieces |
| Consumer Electronics | Mobile‑phone hinge frames; laptop lids; camera bodies; heat‑spreading shells | Enables ultra‑thin, complex geometries with integral EMC shielding; delivers a premium “cold‑metal” feel after plating or painting |
| Appliances & White Goods | Control‑knob spindles; motor‑armature brackets; dispenser levers; decorative trim | Long die life lowers cost per part in high‑volume production; corrosion‑resistant finishes withstand kitchen and laundry environments |
| Building Hardware & Security | Door handles; lock cylinders; window catches; architectural trim | High surface hardness for wear points; crisp detail for aesthetic designs; outstanding drill‑resistance in security cylinders |
| Industrial & Fluid‑Power Equipment | Pneumatic valve bodies; pump housings; gearbox covers | Near‑net casting minimises CNC machining; ZA‑8 alloy provides creep resistance in elevated‑temperature service |
| Medical & Laboratory Devices | Diagnostic‑instrument housings; handheld‑scanner frames; precision adjustment wheels | Tight tolerances maintain alignment of optical and dosing mechanisms; RoHS‑compliant alloys accept antimicrobial coatings |
| Electrical & Lighting | Cable glands; connector shells; LED heat‑sink frames; switch housings | Cast‑in threads and thin fins reduce assembly steps; zinc’s thermal conductivity supports passive cooling |
| Furniture & Décor | Drawer pulls; decorative trims; mirror mounts; adjustable hinges | Replicates fine textures with ease and supports high‑quality chrome, brushed‑nickel, or other premium finishes |









